It depends on the goals of the product and the stage of the product’s lifecycle.
Product managers should be data-driven and use metrics to measure the success of their products. This requires setting clear goals and tracking progress towards those goals over time. Here are some examples of important metrics for different stages:
Early stage: In the early stages of a product’s lifecycle, it’s important to focus on metrics that measure Product Market Fit (PMF). PMF is the degree to which a product satisfies the needs of the market it is targeting. There are several metrics that can be used to measure product-market fit, including:
A) Customer retention rate: This measures the percentage of customers who continue to use the product over time. A high retention rate indicates that customers find the product valuable and are likely to continue using it.
B) Net Promoter Score (NPS): This measures how likely customers are to recommend the product to others. A high NPS indicates that customers are satisfied with the product and are likely to become advocates for it.
C) Customer engagement: This measures how frequently and deeply customers use the product. Metrics like daily active users (DAU) and time spent on the product can indicate how engaged customers are with the product
Growth stage: In the growth stage, it’s important to focus on metrics that measure customer acquisition and conversion. Metrics like cost per acquisition (CPA), conversion rate, and churn rate can help identify areas for improvement in the product’s marketing and user experience.
PMs should focus on ARR (Annual Recurring Revenue) once a product has achieved product-market fit and is in the growth stage. At this stage, the focus shifts from acquiring new customers to retaining existing customers and increasing their lifetime value. ARR is a key metric for SaaS (Software as a Service) and subscription-based businesses.
Maturity stage: In the maturity stage, it’s important to focus on metrics that measure revenue and profitability. Metrics like average revenue per user (ARPU), customer lifetime value (CLTV), and gross margin can provide insight into the product’s financial performance. Market share is the ultimate metric for mature products. This measures the percentage of the total market that the product has captured. A high market share indicates that the product is meeting customer needs and is competitive in the market.
Ultimately, the most important metrics for product leaders to focus on depend on the goals and priorities of the business. It’s important to regularly review and adjust metrics as the product evolves to ensure that they remain relevant and meaningful.
Beware of too many KPIs
One of the biggest challenges big companies face is having too many KPIs across silo’d teams and functions without alignment on a North Star Metric. The result is a bunch of vanity KPIs that don’t quite ladder up to move a shared business objective. The first step in turning around Microsoft’s consumer businesses was addressing this exact challenge.
KPIs are often used to measure operational efficiency and provide insights into how well a particular aspect of a business is performing. But not all KPIs are equal.
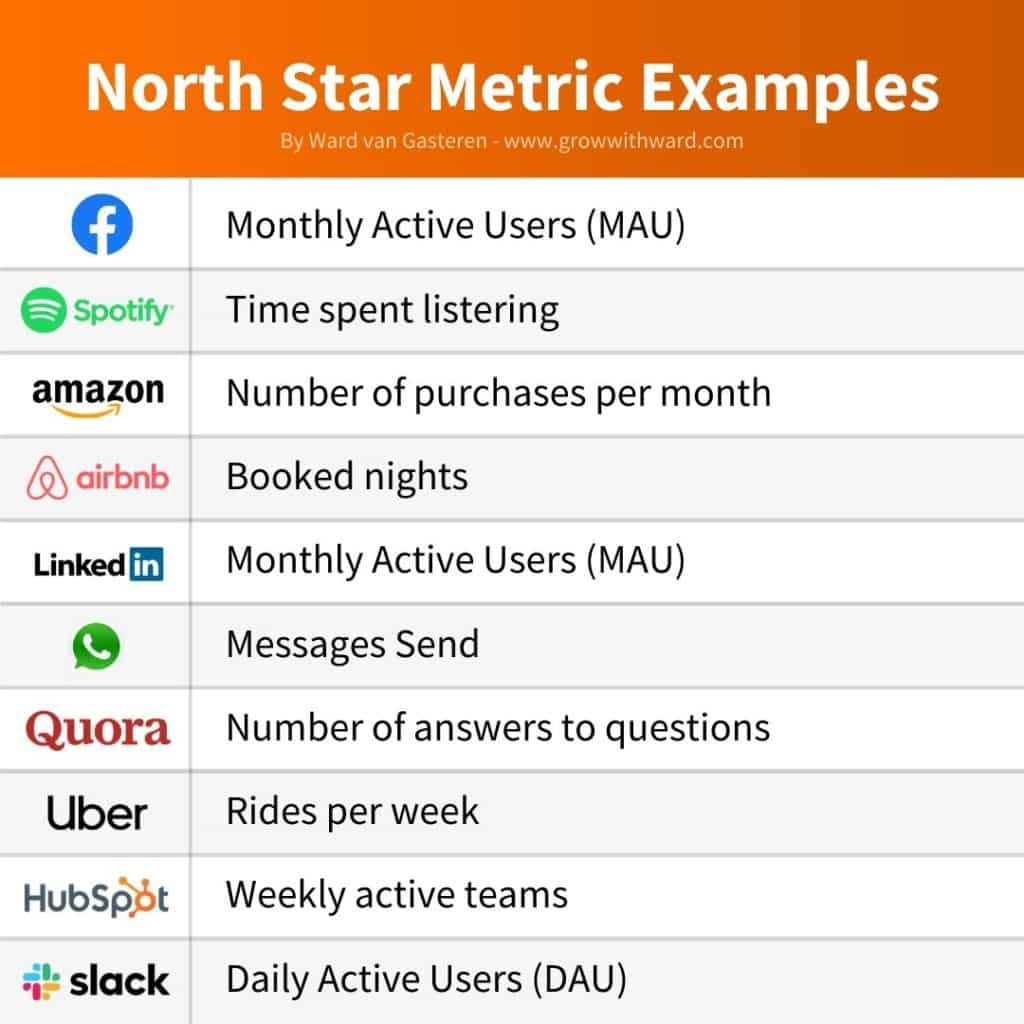
On the other hand, the North Star Metric is a single metric that represents the core value that a product or service delivers to its customers. It is a strategic metric that helps businesses understand their overall health and success. Unlike KPIs, the North Star Metric is meant to be universal across an entire organization and is used to align everyone towards a common goal. It is also used to measure the effectiveness of a company’s overall strategy.
When teams have too many different KPIs, it can lead to confusion, inefficiency, and a lack of focus on the most important goals. Here are some potential negative effects of having too many KPIs:
1) Overwhelming complexity: If there are too many KPIs, it can be difficult to know which ones are the most important or relevant to a particular project or team. This can lead to confusion and a lack of focus on the most important goals.
2) Lack of alignment: When different teams have different KPIs, it can be challenging to align their efforts towards common objectives. This can lead to silos within the organization and a lack of collaboration.
Inefficient resource allocation: If teams are focused on too many KPIs, it can lead to a scattergun approach to resource allocation. This can result in wasted resources on activities that do not contribute to the most important goals.
3) Reduced motivation and engagement: When team members are unclear about what they are working towards, or if they feel that their KPIs are irrelevant, it can lead to reduced motivation and engagement. This can have a negative impact on productivity and morale.
To avoid these negative effects, it is important for teams to focus on a few key KPIs that are directly tied to the organization’s overall objectives. Start with identifying your North Star Metric to align all teams.
#business #marketing #data #growth #engagement #share #success #userexperience #stage

[…] Additional reading : https://liatbenzur.com/2023/03/14/what-are-the-most-important-metrics-for-product-leaders-to-focus-o… […]